|
|
| Power Studies |
- Protective Device Coordination Studies
- Short Circuit Analysis
- Load Flow Analysis
- Arc Flash Hazard Study
- Motor Starting Study
- Transient Stability Analysis
- Generator Start-up Analysis
- Overhead Line - Sag & Tension Analysis
|
|
|
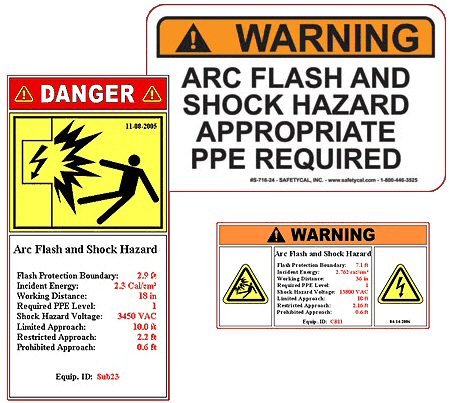
A large number of injuries and fatalities are caused by electrical arcs created during short circuits and switching procedures. Exposure to arcing faults
can cause blindness, ear damage, serious burns, fire, and shock hazards. As a result, NEC 110.8(B)(1)(b) and 130.3(B), as well as NESC ANSI C2-2007
Section 410.A.3 requires you to perform an Arc Flash Hazard Analysis (AFHA). OSHA 29 CFR 1910.132(d) and 1910.335 regulates and enforces these standards.
Pro West Engineering will identify the risk of personnel injury as a result of exposure to incident energy released during an arc flash event for each
specific electrical component, identify the current appropriate ratings of personal protective equipment (PPE), establish the Flash Protection Boundary
as required by NFPA 70E and provide equipment specific environment and chemical arc-flash hazard warning labels per NEC® Section 110.16 requirements.
|
|
Pro West Engineering can perform low/medium/high voltage protective device coordination studies. These studies are performed to
determine the appropriate type of protective device, location and settings for electrical equipment protection.
Electrical systems use fuses and circuit breakers to protect electrical equipment such as conductors, transformers, motors,
and other components. If a failure occurs within this equipment, usually a short circuit results. This study will minimize
the amount of equipment effected by an overcurrent trip.
Short circuits and their effects must be considered in selecting electrical equipment, circuit protection devices and performing out arc flash analysis.
This study is performed in order to determine the magnitude of current flows throughout the power system at critical points during various time
intervals after a fault occurs. These calculations are required for determining the interrupting ratings of your equipment and the coordination of
protective relays, circuit breakers and fuses. The NEC requires that all short circuit interrupting devices be able to handle current beyond what may be imposed by the power system.
|

